Stop Transmission with the Five Pillars of Prevention
The World Health Network (WHN) has released the Five Pillars of Prevention: a multilevel and multilayered approach to reduce the spread of COVID-19. This strategy is effective in combating new variants as they arise, including XBB and multiple BQ versions. By utilizing individual and environmental mitigations together, we can reduce the virus’s impact on individuals, the healthcare system, and the economy.
Public health experts have expressed significant alarm over the “tripledemic” surge in COVID-19, the flu and RSV during the fall and winter of 2022. This increase is driven by a number of factors, including immune system damage due to prior COVID infections, the ongoing emergence of immune-evasive variants (e.g., BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1.5), waning immunity, differential response to booster uptake, and the resumption of pre-pandemic social behavior with minimal precautions against infection. Previous unchecked outbreaks highlighted the devastating consequences of overwhelmed healthcare systems, delays in essential medical services, and resulted in deaths and long COVID consequences that medical professionals are ill-equipped to treat. Both current infections and long term disability also disrupt economic activity.
What is needed now is a better strategy.
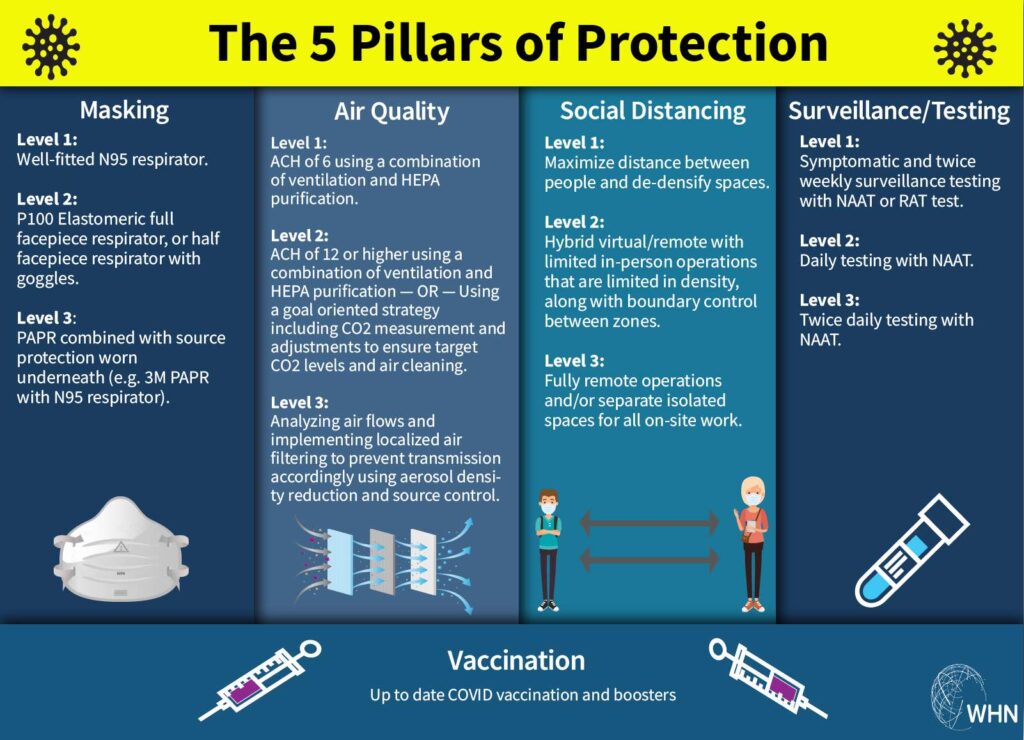
WHN’s Expert Committee argues that many of these anticipated cases can be more readily prevented – so long as multiple types of prevention are used. The Five Pillars of Prevention suggested by the WHN are well known: [2]
1) Masking: Widespread use of high-quality masks (N95 or better) can protect from COVID, and to prevent the spread of the virus.
2) Ventilation: Ventilating shared indoor spaces via frequent air changes and HEPA filtration can reduce the amount of virus present in the air.
3) Social Distancing: Reducing the density of those in indoor spaces is an important step in limiting the amount of virus present in shared spaces. Offering hybrid and remote options, when possible, is an important step in keeping workplaces and other shared spaces safe.
4) Testing: Because it’s possible to be contagious before showing symptoms, testing and surveillance are key components in limiting the spread of COVID-19. PCR tests are preferred due to higher accuracy and ability to detect the virus in the early stages of infection.
5) Vaccination: Vaccination is a key step individuals can take to protect themselves and their community from severe illness. Vaccination is most effective as a public health tool when paired with other mitigation strategies that limit the evolution of the virus and its ability to evade existing vaccines.
Significantly, if there are people or organizations that cannot do one or other of these measures, the other ones can be strengthened to make up the difference.
For example, for people who cannot do social distancing, masking can be improved to the level of elastomeric masks. Elastomeric masks are better than N95 masks, and are less expensive because they can be reused many times.
Alternatively, higher levels of ventilation, or more frequent testing.
Environmental protections such as good ventilation reduce the amount of individual action such as masking that are needed in places where people have to go to work, or people must take to protect themselves and access essential services. For example, increasing the air filtering rate from 6 air exchanges per hour to 12 or more can make a significant difference.
Combining higher levels of any one of the measures can make up for lower levels of another. This provides different places and different industries with options that can better suit them while providing the same level of protection.
The five pillars are effective against all COVID variants, as well as other respiratory viruses of concern (e.g. RSV, influenza) and environmental pollutants.
Combining the Five Pillars of Prevention through individual and community action not only does more to reduce transmission but also enables more flexibility on lowering one of the measures while raising another. Any one Pillar of Prevention must contribute only part of what is needed to reduce the spread of COVID. Multiple protections reduce the impact of any one method failing or being unavailable. Reducing transmission via the five pillars will support the effectiveness of our current vaccines and treatments for COVID-19 and is essential to preserving individual health, and the functionality of the healthcare system and the economy.