Omicron Is Dangerous Because It Is Fast
Published on December 15, 2021
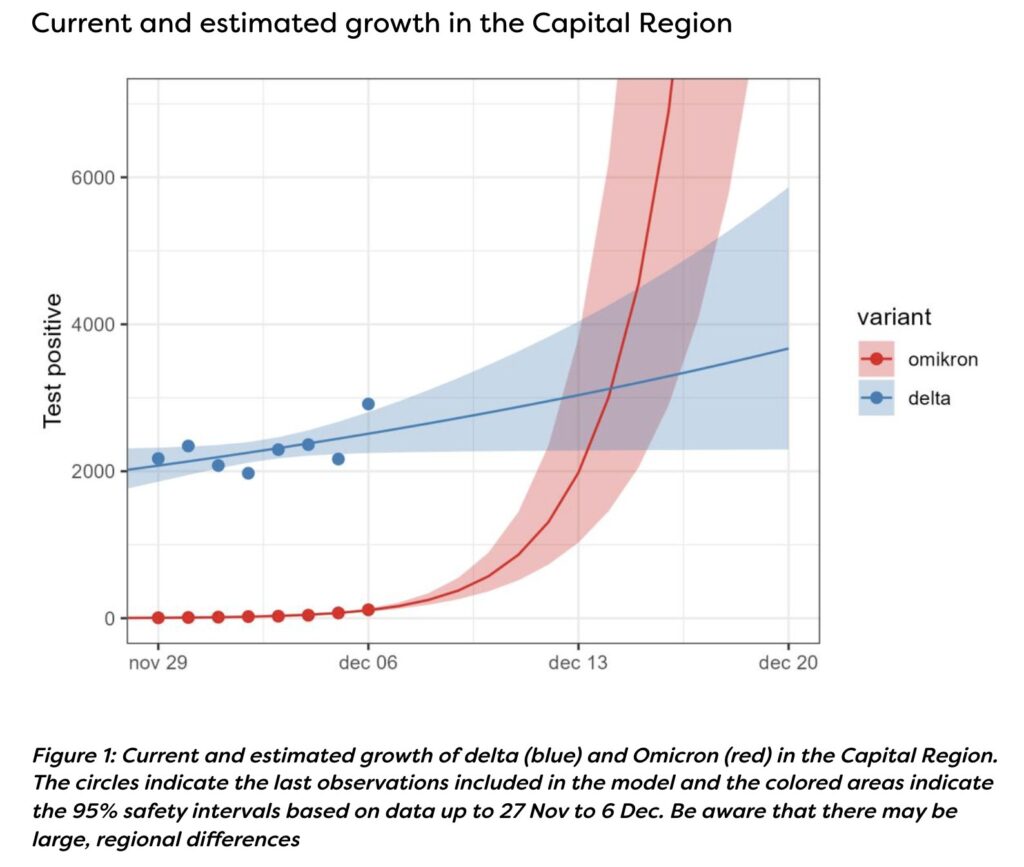
Transmission beats mortality by a long shot. If Omicron transmission increases by a factor of 2, a decrease in mortality of 50% is almost negligible for the harm created per month.
We urge governments and communities to focus on stopping transmission now and relax restrictions only if we discover evidence that Omicron is harmless.
Guidance
How to have a safe Christmas: the ultimate checklist (English) – Infographic (WHN)
(Deutsch)
(Français)
(Español)
Resources
Omicron
Herd immunity crumbles against Omicron, as population-level evidence suggests Omicron variant evades immunity from prior infection
Omicron tears through London. (Dr. Rob Whitehurst)
Denmark sees more hospitalizations in Omicron than Delta, and publishes stark projection of Omicron’s rapid spread (Eric Feigl-Ding)
Omicron infecting more children than previous strains and driving pediatric hospitalizations, according to Director of Centre for Epidemic Response in South Africa
South Africa’s Tulio de Oliveira “Face the Nation” interview, December 12, 2021 (CBS)
Risk assessment upgraded to “red” due to high growth advantage vs. delta and high immune evasion according to UK Health Security Agency
9 December 2021 Risk assessment for SARS-CoV-2 variant: Omicron (UK Health Security Agency)
Omicron variant growth and wastewater surveillance details in England
Technical Briefing 31 (UK Health Security Agency)
Wastewater monitoring in eastern Massachusetts shows increased viral RNA with exponential growth pattern
Population health insights powered by sewage (Biobot Analytics)
Hong Kong places travel restrictions on all UK and US travelers, as well as travelers from 73 other nations, subject to 21 days of compulsory quarantine
COVID-19 Information (U.S. Consulate General Hong Kong & Macau)
Policy
The need for urgent public health action beyond vaccines
COVID-19 Commission Task Force On Public Health Measures To Suppress the Pandemic (The Lancet)
Nonpharmaceutical Interventions Remain Essential to Reducing Coronavirus Disease Burden Even in a Well-Vaccinated Society
NPIs and vaccines work synergistically to reduce disease burden (Open Forum Infectious Diseases)
Socioeconomically disadvantaged children found to carry highest burden of infection – Improving equity between groups important to limiting spread of COVID-19
Racial and/or Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Children (Pediatrics)
Significant reduction in SARS-CoV-2 incidence found among persons experiencing homelessness when provided with protective housing as compared with city shelters
Isolation policies of 2 weeks may be insufficient as 10% of cases may have incubation period longer than WHO’s current recommended medical observation period of 14 days
Modeling study finds COVID incubation period can be longer than 14 days (BMC Public Health)
Economy
More than half a billion pushed into extreme poverty due to pandemic related health costs
Pandemic likely to halt two decades of global progress towards Universal Health Coverage (United Nations)
Nations that applied the elimination strategy tended to achieve better health outcomes in relation to their peers without having to accept lower economic growth
The impact of government responses to the COVID-19 pandemic on GDP growth: Does strategy matter? (PLoS ONE)
UK faces food supply chain crisis without Government action
Supply chain ‘must be fixed urgently’ to ensure food security in the UK (Guardian)
Research shows saving lives protects the economy
If the world fails to protect the economy, COVID-19 will damage health not just now but also in the future (Nature Medicine)
Asia economists cautiously optimistic even amid Omicron fears due to region’s containment strategies, citing India and Indonesia case declines
Higher vaccination rates and smaller waves of infection in Asia may boost region’s economic resilience relative to western peers (South China Morning Post)
Mitigation
Max Planck Institute research underscores the remarkable efficacy and importance of masks in controlling infection
Detailed study shows the maximum risks of being infected by the coronavirus for different scenarios with and without masks (Max Planck Institute)
National Guard deployed to multiple US states as ongoing hospital capacity crisis deepens (NYT)
Outbreak at 99% vaccinated Middlebury College forces move to remote instruction (NYT); Cornell U. follows with outbreak of 500 (CNN)
“Contact tracing in combination with mask wearing in public places can have a strong and immediate effect in bringing down epidemic growth”
Harnessing peak transmission around symptom onset for non-pharmaceutical intervention and containment of the COVID-19 pandemic (Nature Communications)
Social and financial support programs help minimize health disparities and adverse consequences of pandemic control measures
Mitigating the wider health effects of covid-19 pandemic response (BMJ)
Reopening face-to-face schooling during lockdowns risks increased transmission
Estimating the impact of reopening schools on the reproduction number of SARS-CoV-2 in England (BMC Medicine)
Thoughts from China on using containment measures to slow the growth of outbreaks
Effective containment explains subexponential growth in recent confirmed COVID-19 cases in China (Science)
In Community,
-The WHN